V. ΠΕΙΡΑΜΑΤΑ ΠΡΟΗΓΜΕΝΗΣ ΦΥΣΙΚΗΣ
(Advanced Physics Lab. Experiments)
1. Diode Laser Spectroscopy
• Explore Doppler-Free Spectroscopy of Rubidium Gas
• Determine Resonant Faraday Rotation in Rb Vapor
• Examine Stabilized Diode Laser
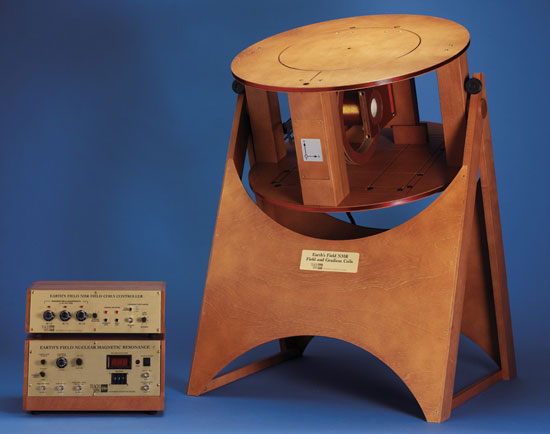
2. Earth's Field EFNMR 1-A
• Measure Proton and Fluorine NMR
• Discover Curie's Law and Spin-Lattice Relaxation
• Cancel Gradients Due to Local Effects, Observe Natural FID
• Study Field Dependence of NMR
![]()
3. Earth's Field w/ Gradient/Field Coil EFNMR 1-B
Gradient Coils:
• Homogenize Local Earth's Magnetic Field
• Permit Measurement of Spin-Spin Relaxation (T2)
• Demonstrate One-Dimensional NMR Imaging (MRI)
• Generate Observable (and Audible) Spin-Echoes
Helmholtz Coils:
• Permit Absolute Measurement of Nuclear Magnetic Moments
• Provide Fields for Experiments on 31P and 2H Nuclei
• Show Quantitatively that Magnetic Fields Add as Vectors
![]()
4. Fabry-Perot Cavity 780 ± 40 nm
• Calibrate Optical Frequency Scale of Tunable Laser
• Investigate and Employ Cavity Mode Structure
![]()
5. Faraday Rotation
• Measure Verdet Constant of Transparent Solids
and Liquids
• Study Interaction of Light, Matter, and Magnetic Fields
![]()
6. Hall Effect Probe
• Measure the Magnetic Fields You Teach
• High Sensitivity 2 x 10-3 mT
![]()
7. Magnetic Force
• Discover Magnetic Force Depends on Field Gradient
• Measure µ from Magnetic Force
![]()
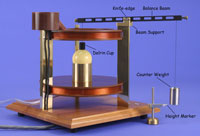
8. Magnetic Torque
• Measure µ Five Independent Ways
• Observe "Classical" Magnetic Resonance
![]()
9. Magnetic Torque's Magnetic Force Balance
Now part of MT1-B
• Measure µ of Sphere with Magnetic Force
![]()
10. Modern Interferometry
• Sagnac, Michelson, Mach-Zehnder Configurations
• Thermal Expansion, Magneto-Striction, Electro-Optic
Effect and more
• Proprietary Flexure Mirror Mounts
![]()
11. Muon Physics
• Measure Muon Lifetime
• Demonstrate Relativistic Time Dilation
![]()
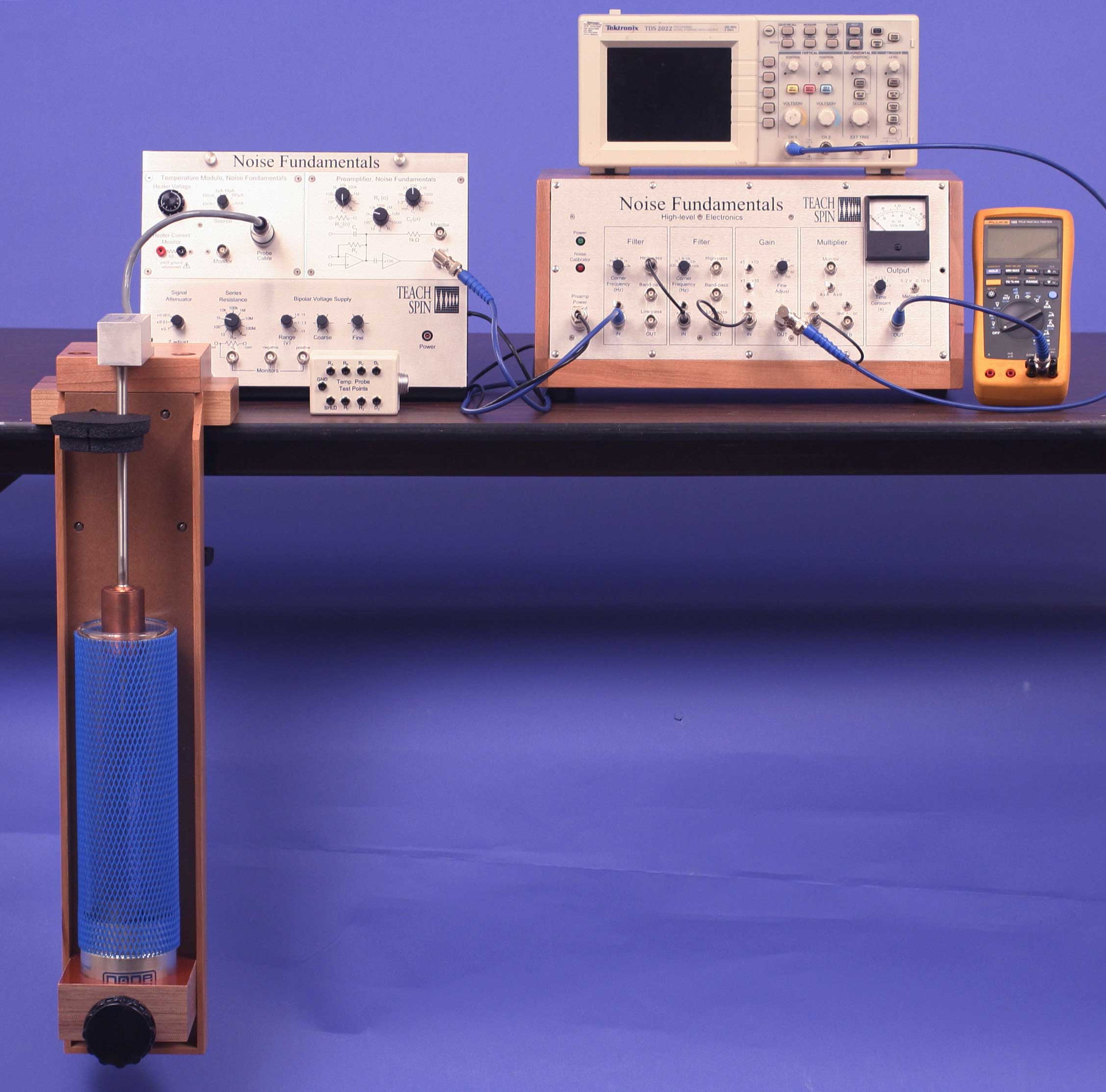
12. Noise Fundamentals
• Detect and quantify Johnson noise, the ‘Brownian motion’ of electrons
• Deduce Boltzmann’s constant, kB, from the temperature dependence of
Johnson Noise
• Observe and quantify shot noise in order to measure the fundamental
charge ‘e’.
![]()
13. Optical Pumping of Rubidium Vapor
• Precisely Measure Hyperfine Structure
• Study Rabi Oscillations
![]()
14. Instructional Pulsed/CW Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
Spectrometer
• 15 MHz Proton Pulsed NMR
• Research Grade Measurements of T1 and T2.
![]()
15. Quantum Analogs
Acoustic models of:
- Hydrogen Atom
- Hydrogen Molecule
- Lowering symmetry to lift degeneracy
- Band gaps in semiconductors
![]()
16. Signal Processor/Lock-In Amplifier
• A Teaching Lock-In
• Multiple Electronic Strategies for Processing
Electronic Signals
• Noise Generator and Test Signals Built-In
![]()
17. Sonoluminescence
• Acoustically Generated Photons
• Study Acoustic Resonance
![]()
18. Torsional Oscillator
• fully instrumented test-bed for investigating simple harmonic motion
• variable torsion constant and rotational inertia
• non-contact precision analog sensors provide angular position and velocity
• damping options range from constant to velocity dependent and include a v2-
friction regime
• magnetic torque drive accommodates arbitrary drive waveforms
• resonant behavior in time and frequency domains with "Q" ranging from
less than 1 to more than 100.
![]()